一些新的和遗忘的知识点
根据论文中的定义,u x = 1 A ∮ u d y ≈ 1 A ∑ i = 1 n 1 2 ( u i + 1 + u i ) ( y i + 1 − y i ) u_x=\frac{1}{A}\oint u \text{d}y \approx \frac{1}{A} \sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{1}{2}\left ( u_{i+1}+u_i\right )\left ( y_{i+1}-y_i\right ) u x = A 1 ∮ u d y ≈ A 1 ∑ i = 1 n 2 1 ( u i + 1 + u i ) ( y i + 1 − y i ) u y = − 1 A ∮ u d x u_y=-\frac{1}{A}\oint u \text{d}x u y = − A 1 ∮ u d x v x = 1 A ∮ v d y v_x=\frac{1}{A}\oint v \text{d}y v x = A 1 ∮ v d y v y = − 1 A ∮ v d x v_y=-\frac{1}{A}\oint v \text{d}x v y = − A 1 ∮ v d x
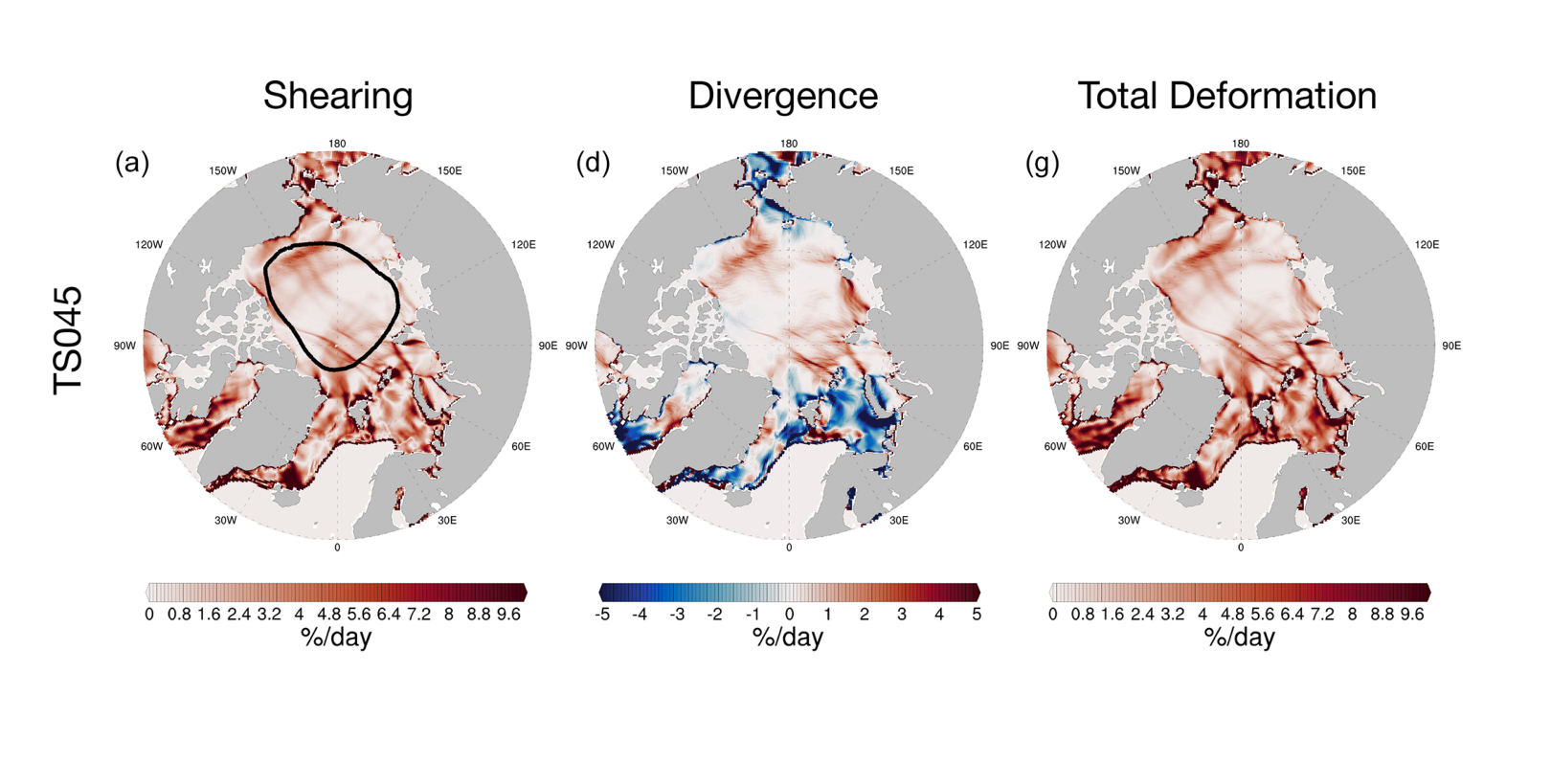
剪切率 ε ˙ shear = ( u x − v y ) 2 + ( u y + v x ) 2 \dot{\varepsilon}_{\textrm{shear}}=\sqrt{\left ( u_{x}-v_{y}\right )^2+\left ( u_{y}+v_{x}\right )^2} ε ˙ shear = ( u x − v y ) 2 + ( u y + v x ) 2 ε ˙ div = u x + v y \dot{\varepsilon }_{\textrm{div}} = u_x+v_y ε ˙ div = u x + v y ε ˙ tot = ε ˙ shear 2 + ε ˙ div 2 \dot{\varepsilon }_{\textrm{tot}}=\sqrt{\dot{\varepsilon }_{\textrm{shear}}^{2}+\dot{\varepsilon }_{\textrm{div}}^{2}} ε ˙ tot = ε ˙ shear 2 + ε ˙ div 2
Strain rate is the rate of deformation caused by strain in a material within a corresponding time. This gauges the rate where distances of materials change within a respective period of time.
# B-gridCSIM uses a generalized orthogonal B-grid , where tracer quantities are located at the center of the grid cells, and velocities are located at the corners. The internal ice stress tensor takes four different values within a grid cell. Tracer quantities in the ice model include ice and snow area, volume, energy and temperature. The grid comprised of the center points of the grid cells is referred to as the “T grid”. The “U grid” is comprised of the ponts at the northeast corner of the corresponding cell on the T grid. Quantities that are defined on the U grid include ice and ocean dynamics variables.
计算应变速率所需要的速度是定义在 U grid 上的,也就是每个 cell 的右上(东北)角。
参考页面
# 概率分布# 随机变量的定义设( Ω , F , P ) \left ( \Omega,\mathscr{F},P\right ) ( Ω , F , P ) ξ = ξ ( ω ) \xi =\xi(\omega ) ξ = ξ ( ω ) Ω \Omega Ω
{ ω : ξ ( ω ) < x } ∈ F , ∀ x ∈ R , \left \{ \omega:\xi(\omega) < x \right \} \in \mathscr{F}, \forall x \in \mathbb{R}, { ω : ξ ( ω ) < x } ∈ F , ∀ x ∈ R ,
则称ξ ( ω ) \xi(\omega) ξ ( ω )
时常将ξ ( ω ) , { ω : ξ ( ω ) < x } \xi(\omega), \left \{ \omega:\xi(\omega) < x \right \} ξ ( ω ) , { ω : ξ ( ω ) < x } ξ , { ξ < x } \xi, \{\xi < x\} ξ , { ξ < x }
# 分布函数F ( x ) = F { ( − ∞ , x ) } = P { ξ < x } , x ∈ R F(x)=\mathbf{F} \{(-\infty,x)\} =P\{\xi < x\}, x \in \mathbb{R} F ( x ) = F { ( − ∞ , x ) } = P { ξ < x } , x ∈ R ξ \xi ξ ξ \xi ξ F ( x ) F(x) F ( x ) ξ ∼ F ( x ) \xi \sim F(x) ξ ∼ F ( x ) F ξ ( x ) F_\xi(x) F ξ ( x ) ξ \xi ξ
在论文中称其为 Cumulative Density Functions(累积密度函数),定义为
c d f ( x ) = F { ( x , ∞ ) } = P { ξ > x } , x ∈ R cdf(x)=\mathbf{F} \{(x,\infty)\} =P\{\xi > x\}, x \in \mathbb{R} c d f ( x ) = F { ( x , ∞ ) } = P { ξ > x } , x ∈ R P ( x ) ∼ c d f ( x ) P(x) \sim cdf(x) P ( x ) ∼ c d f ( x )
# 密度函数若存在函数p ( x ) p(x) p ( x ) p ( x ) > 0 , ∫ R p ( x ) d x = 1 p(x)>0, \int_{\mathbb{R}} p(x) \text{d}x=1 p ( x ) > 0 , ∫ R p ( x ) d x = 1 F ( x ) = ∫ − ∞ x p ( t ) d t , x ∈ R F(x)=\int_{-\infty}^x p(t) \text{d}t, x\in \mathbb{R} F ( x ) = ∫ − ∞ x p ( t ) d t , x ∈ R ξ \xi ξ p ( x ) p(x) p ( x )
# 期望离散型:对概率分布 p i = P { ξ = x i } , i = 1 , 2 , . . . p_i=P\{\xi=x_i\}, i=1,2,... p i = P { ξ = x i } , i = 1 , 2 , . . . ∑ i ∣ x i ∣ p i < + ∞ \sum_i |x_i|p_i < +\infty ∑ i ∣ x i ∣ p i < + ∞
E ( ξ ) = ∑ i x i p i E(\xi)=\sum_i x_i p_i E ( ξ ) = ∑ i x i p i ∫ − ∞ + ∞ ∣ x ∣ p ( x ) d x < + ∞ \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} |x|p(x)\text{d}x < +\infty ∫ − ∞ + ∞ ∣ x ∣ p ( x ) d x < + ∞ E ( ξ ) = ∫ − ∞ + ∞ x p ( x ) d x E(\xi)=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} xp(x)\text{d}x E ( ξ ) = ∫ − ∞ + ∞ x p ( x ) d x
# 方差D ( ξ ) = E ( [ ξ − E ( ξ ) ] 2 ) = ∫ − ∞ + ∞ [ x − E ( ξ ) ] 2 p ( x ) d x D(\xi)=E (\left [ \xi-E(\xi) \right ]^2) = \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} \left[ x-E(\xi) \right]^2 p(x)\text{d}x D ( ξ ) = E ( [ ξ − E ( ξ ) ] 2 ) = ∫ − ∞ + ∞ [ x − E ( ξ ) ] 2 p ( x ) d x D ( ξ ) = E ( ξ 2 ) − [ E ( ξ ) ] 2 D(\xi)= E(\xi^2)-\left[ E(\xi)\right]^2 D ( ξ ) = E ( ξ 2 ) − [ E ( ξ ) ] 2
k 阶原点矩(the k th k^{\text{th}} k th E ( ξ k ) E(\xi^k) E ( ξ k ) k th k^{\text{th}} k th E ( [ ξ − E ( ξ ) ] k ) E(\left[ \xi-E(\xi) \right]^k) E ( [ ξ − E ( ξ ) ] k ) 1 N ∑ i = 1 N x i k \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N} x_i^k N 1 ∑ i = 1 N x i k
参考页面